Dr Anatoli Nachev
Lecturer in Business Information Systems
J.E. Cairnes School of Business and Economics, University of Galway



Anatoli's research and teaching are in the areas of business analytics, data mining and machine learning. His recent and current work is mainly focused on the application of machine learning to socially significant areas such as employment and the labour market, poverty, access to the Irish health system, and unmet healthcare needs. He is particularly interested in the study and measurement of socio-economic drivers and factors in this context using machine learning techniques such as neural networks, support vector machines, and ensemble techniques, among others.
Anatoli's work contributes to these SDGs

Anatoli's teaching supports several SDGs by promoting innovation and infrastructure development, supporting quality education, fostering economic growth and decent work, addressing urban challenges, and fostering partnerships for sustainable development. Understanding modern data communication technologies is crucial for advancing infrastructure, fostering innovation, and promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialisation. By equipping students with knowledge of network and internet concepts, as well as network security technologies, his teaching contributes to SDG 9 by promoting technological progress and innovation.
Key Target: 9.0 Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation

Teaching

Advanced Application Programming (Java) The aim of the course is to develop knowledge and competence in object-oriented programming for the business environment using the Java programming language. Students have opportunities through the coursework and the broader student experience to develop a wide range of knowledge and ability to solve new challenges and problems. Students also have opportunity to appreciate ethical and professional standards, integrity and responsibility. By providing quality education in this field, this course contributes to the advancement of SDG 4, which aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Competence in object-oriented programming, particularly in Java, enhances employability and fosters economic growth. It equips students with skills relevant to the business environment, aligning with the goal of promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all (SDG 8).
Object-oriented programming skills are fundamental to innovation and technological advancement. By fostering competence in Java programming, the course contributes to building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and fostering innovation (SDG 9).
Supporting Targets: 4.7 Education for sustainable development and global citizenship; 8.3 Promote policies to support job creation and growing enterprises; 9.B Support domestic technology development and industrial diversification
Business Modelling and Analytics The objective of this course is to develop students' understanding of the role of business analytics in decision-making and equip them with solutions used to create scenarios, understand realities and predict future states. The course focuses on descriptive analytics used to gain insight from historical data, predictive analytics used to forecast future business performance, and prescriptive analytics used to recommend decisions using optimisation, simulation, etc. Students are introduced to core concepts and technologies of business analytics, such as modelling, analysis, optimisation; data exploration and data mining; forecasting models; decision trees; neural networks; clustering techniques; etc. The course uses real business cases to illustrate the application and interpretation of these methods.
Business analytics plays a crucial role in improving industrial processes, fostering innovation, and enhancing infrastructure efficiency. By equipping students with skills in descriptive, predictive and prescriptive analytics, the course contributes to advancing SDG 9 by promoting technological progress and innovation.
Effective decision-making based on data-driven insights is essential for building sustainable and resilient cities and communities. By teaching students how to analyse data and forecast future trends, the course supports SDG 11 by helping to create cities and communities that are inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable.
Business analytics can help optimise resource usage, minimise waste and improve production efficiency, thereby contributing to sustainable consumption and production patterns. By introducing students to techniques such as optimisation and simulation, the course aligns with SDG 12's objective of promoting responsible consumption and production practices.
Supporting Targets: 9.B Support domestic technology development and industrial diversification; 11.6 Reduce the environmental impacts of cities; 12.6 Encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices and sustainability reporting
Business Data Communications The objective of this course is to develop in students an understanding of the fundamentals of modern data communication technologies and to combine them with applications and practices related to a business environment. Topics include network and internet concepts and technologies, network security technologies, problems and solutions.
Proficiency in data communication technologies is essential for creating decent work opportunities and fostering economic growth, particularly in the digital economy. By equipping students with relevant skills and knowledge, the course contributes to SDG 8 by promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
Supporting Targets: 4.7 Education for sustainable development and global citizenship; 8.3 Promote policies to support job creation and growing enterprises; 9.B Support domestic technology development and industrial diversification
Data Science and Big Data Analytics This module aims to provide students with knowledge required to become active contributors to big data analytics projects and to develop specific skills needed to use and implement big data analytics technology and tools, create models, and identify insights that can lead to actionable results. Topics include big data technology and tools, big data analytics project lifecycle, creating business value with big data. The module focuses on how technologies can be integrated and used in a business intelligence environment through case studies of big data applications and reframing a business challenge as an analytics challenge.
Understanding big data analytics technology and tools is crucial for advancing technological infrastructure and fostering innovation, which are key components of SDG 9. By equipping students with the knowledge and skills needed for big data analytics projects, the module contributes to promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialisation. Proficiency in big data analytics technology and tools is essential for creating decent work opportunities and fostering economic growth, particularly in the digital economy. By developing the specific skills needed to use and implement big data analytics, the module contributes to SDG 8 by promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
Big data analytics can provide valuable insights for addressing urban challenges and promoting sustainable development in cities. By focusing on creating business value with big data and examining case studies of big data applications, the module supports SDG 11 by contributing to the development of sustainable cities and communities. By integrating big data analytics technologies and tools into a business intelligence environment and using case studies to illustrate their application, the module fosters partnerships and knowledge-sharing, contributing to the broader agenda of SDG 17.
Supporting Targets: 4.7 Education for sustainable development and global citizenship; 8.3 Promote policies to support job creation and growing enterprises; 11.6 Reduce the environmental impacts of cities, 17.6 Knowledge sharing and cooperation for access to science, technology and innovation
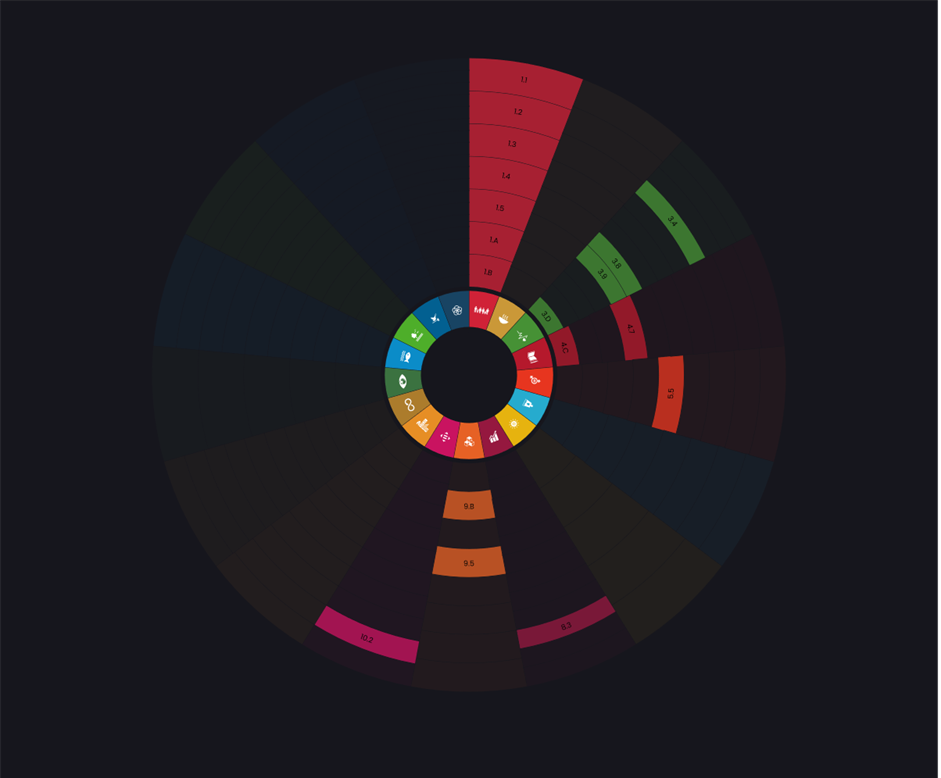
Direct impact SDG Targets
1.1 - Eradicate extreme poverty
1.2 - Reduce poverty by at least 50%
1.3 - Implement social protection systems
1.4 - Equal rights to ownership, basic services, technology and economic resources
1.5 - Build resilience to environmental, economic and social disasters
1.A - Mobilize resources to implement policies to end poverty
1.B - Create pro-poor and gender-sensitive policy frameworks
3.4 - Reduce mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote mental health
3.8 - Achieve universal health coverage
3.9 - Reduce illnesses and death from hazardous chemicals and pollution
3.D - Improve early warning systems for global health risks
4.7 - Education for sustainable development and global citizenship
4.C - Increase the supply of qualified teachers in developing countries
5.5 - Ensure full participation in leadership and decision-making
8.3 - Promote policies to support job creation and growing enterprises
9.5 - Enhance research and upgrade industrial technologies
9.B - Support domestic technology development and industrial diversification
10.2 - Promote universal social, economic and political inclusion
Research

Featured Publications
|
References |
SDGs |
|
Nachev, A. (2023). Analysis of Factors Influencing the Severity of Coronavirus Symptoms Using Predictive Modeling. In Proc. of International Conference Artificial Intelligence, ICAI’23, USA. |
3.8, 3.D |
|
Teodosiev, T., Nachev, A. (2023). Role of the Algorithm in Introductory Programming Courses. In Ajaykumar, B. S. ed. Advances in Engineering Research and Technology, Singapore: RM Research International. ISBN: 978-981-18-7797-1. |
8.1 |
|
Nachev, A. (2022). Assessment of Healthcare Services Using Models Based on Support Vector Machines. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, IJEAT, 12(2). |
3.8 |
|
Nachev, A. (2022). Exploring Irish Healthcare: Identifying Needs for Services by Decision Tree Modelling. In Proc. of International Conference Artificial Intelligence, ICAI’22, USA. |
3.8 |
|
Nachev, A., Teodosiev, T. (2018). Analysis of Employment Data Using Support Vector Machines. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research (IJAER), 13(18). |
8.5 |